Full Stack Testing¶
Why?¶
The idea behind “fullstack” testing is to fill a gap between unit + functional tests and Tempest. Tempest tests are expensive to run, and operate only through the REST API. So they can only provide an explanation of what went wrong gets reported to an end user via the REST API, which is often too high level. Additionally, Tempest requires an OpenStack deployment to be run against, which can be difficult to configure and setup. The full stack testing addresses these issues by taking care of the deployment itself, according to the topology that the test requires. Developers further benefit from full stack testing as it can sufficiently simulate a real environment and provide a rapidly reproducible way to verify code as you’re still writing it.
How?¶
Full stack tests set up their own Neutron processes (Server & agents). They assume a working Rabbit and MySQL server before the run starts. Instructions on how to run fullstack tests on a VM are available in our TESTING.rst.
Each test defines its own topology (What and how many servers and agents should be running).
Since the test runs on the machine itself, full stack testing enables “white box” testing. This means that you can, for example, create a router through the API and then assert that a namespace was created for it.
Full stack tests run in the Neutron tree with Neutron resources alone. You may use the Neutron API (The Neutron server is set to NOAUTH so that Keystone is out of the picture). VMs may be simulated with a container-like class: neutron.tests.fullstack.resources.machine.FakeFullstackMachine. An example of its usage may be found at: neutron/tests/fullstack/test_connectivity.py.
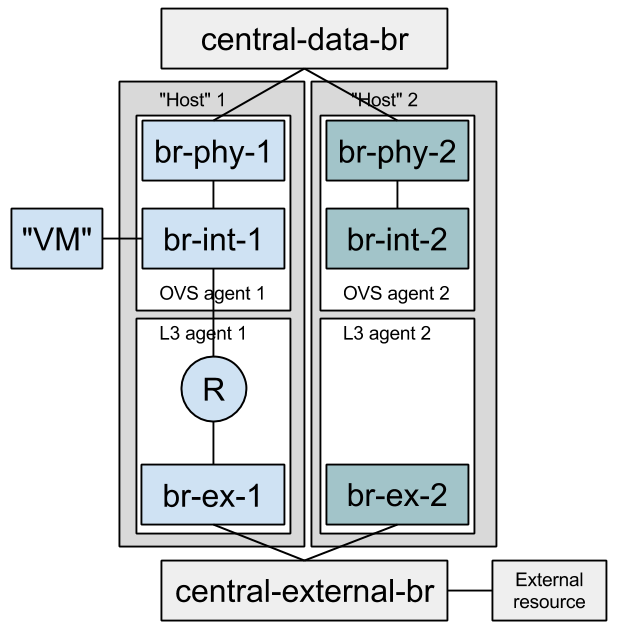
Full stack testing can simulate multi node testing by starting an agent multiple times. Specifically, each node would have its own copy of the OVS/DHCP/L3 agents, all configured with the same “host” value. Each OVS agent is connected to its own pair of br-int/br-ex, and those bridges are then interconnected.
When?¶
- You’d like to test the interaction between Neutron components (Server and agents) and have already tested each component in isolation via unit or functional tests. You should have many unit tests, fewer tests to test a component and even fewer to test their interaction. Edge cases should not be tested with full stack testing.
- You’d like to increase coverage by testing features that require multi node testing such as l2pop, L3 HA and DVR.
- You’d like to test agent restarts. We’ve found bugs in the OVS, DHCP and L3 agents and haven’t found an effective way to test these scenarios. Full stack testing can help here as the full stack infrastructure can restart an agent during the test.
Prerequisites¶
Fullstack test suite assumes 240.0.0.0/3 range in root namespace of the test machine is available for its usage.
Short Term Goals¶
- Multinode & Stability:
- Convert the L3 HA failover functional test to a full stack test
- Write a test for DHCP HA / Multiple DHCP agents per network
Write DVR tests
Write additional L3 HA tests
Write a test that validates L3 HA + l2pop integration after https://bugs.launchpad.net/neutron/+bug/1365476 is fixed.
Write a test that validates DVR + L3 HA integration after https://bugs.launchpad.net/neutron/+bug/1365473 is fixed.
After these tests are merged, it should be fair to start asking contributors to add full stack tests when appropriate in the patches themselves and not after the fact as there will probably be something to copy/paste from.
Long Term Goals¶
- How will advanced services use the full stack testing infrastructure? Full stack tests infrastructure classes are expected to change quite a bit over the next coming months. This means that other repositories may import these classes and break from time to time, or copy them in their repositories instead. Since changes to full stack testing infrastructure is a given, XaaS repositories should be copying it and not importing it directly.
- Currently we configure the Neutron server with the ML2 plugin and the OVS mechanism driver. We may modularize the topology configuration further to allow to rerun full stack tests against different Neutron plugins or ML2 mechanism drivers.
- Add OVS ARP responder coverage when the gate supports OVS 2.1+