Baremetal Environment¶
TripleO can be used in an all baremetal environment. One machine will be used for Undercloud, the others will be used for your Overcloud.
Minimum System Requirements¶
To deploy a minimal TripleO cloud with TripleO you need the following baremetal machines:
- 1 Undercloud
- 1 Overcloud Controller
- 1 Overcloud Compute
For each additional Overcloud role, such as Block Storage or Object Storage, you need an additional baremetal machine.
The baremetal machines must meet the following minimum specifications:
- multi-core CPU
- 8 GB memory
- 60 GB free disk space
Larger systems are recommended for production deployments, however.
TripleO is supporting only the following operating systems:
- RHEL 7.1 x86_64 or
- CentOS 7 x86_64
Preparing the Baremetal Environment¶
Networking¶
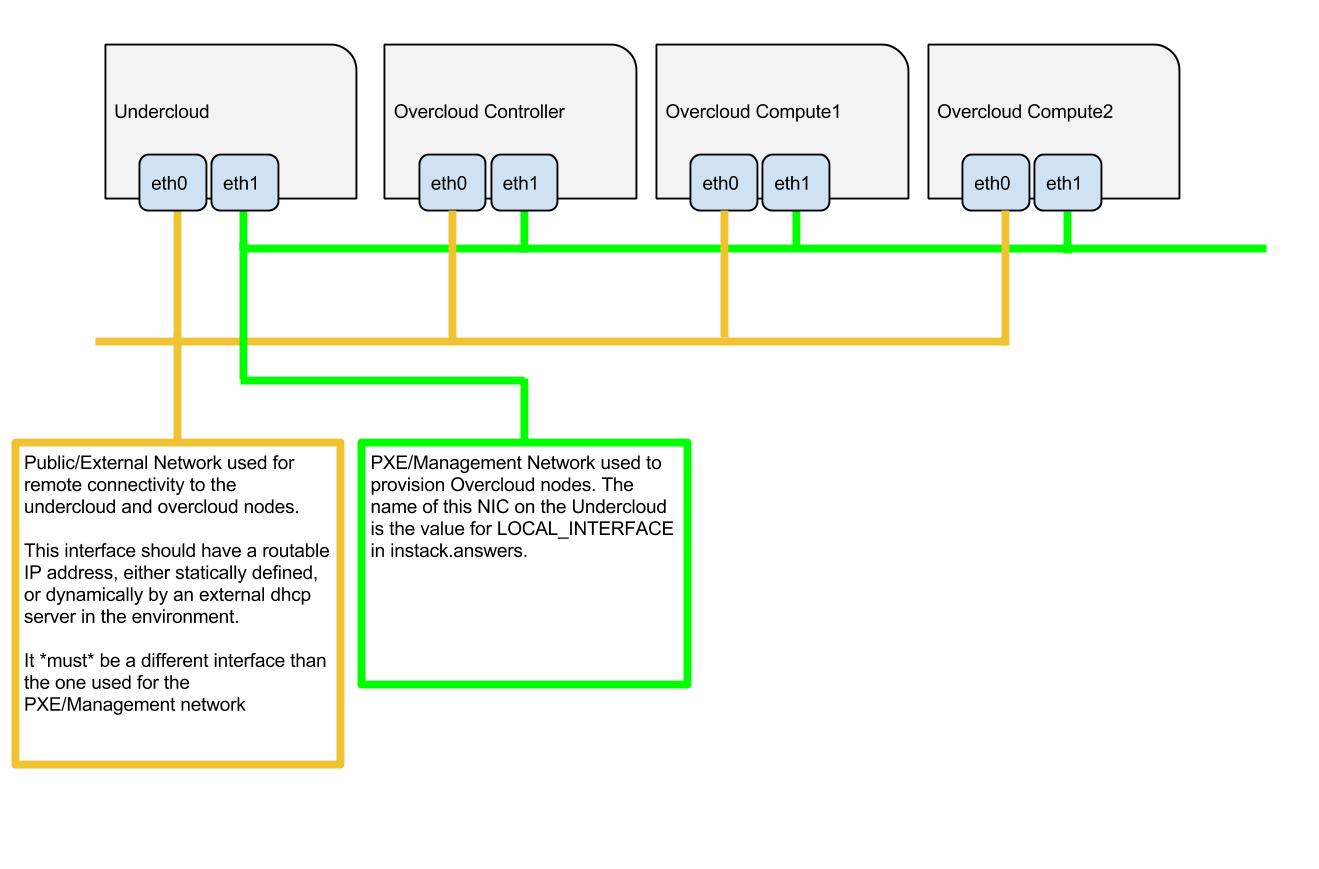
The overcloud nodes will be deployed from the undercloud machine and therefore the machines need to have have their network settings modified to allow for the overcloud nodes to be PXE boot’ed using the undercloud machine. As such, the setup requires that:
- All overcloud machines in the setup must support IPMI
- A management provisioning network is setup for all of the overcloud machines. One NIC from every machine needs to be in the same broadcast domain of the provisioning network. In the tested environment, this required setting up a new VLAN on the switch. Note that you should use the same NIC on each of the overcloud machines ( for example: use the second NIC on each overcloud machine). This is because during installation we will need to refer to that NIC using a single name across all overcloud machines e.g. em2
- The provisioning network NIC should not be the same NIC that you are using for remote connectivity to the undercloud machine. During the undercloud installation, a openvswitch bridge will be created for Neutron and the provisioning NIC will be bridged to the openvswitch bridge. As such, connectivity would be lost if the provisioning NIC was also used for remote connectivity to the undercloud machine.
- The overcloud machines can PXE boot off the NIC that is on the private VLAN. In the tested environment, this required disabling network booting in the BIOS for all NICs other than the one we wanted to boot and then ensuring that the chosen NIC is at the top of the boot order (ahead of the local hard disk drive and CD/DVD drives).
- For each overcloud machine you have: the MAC address of the NIC that will PXE boot on the provisioning network the IPMI information for the machine (i.e. IP address of the IPMI NIC, IPMI username and password)
Refer to the following diagram for more information
Setting Up The Undercloud Machine¶
Select a machine within the baremetal environment on which to install the undercloud.
Install RHEL 7.1 x86_64 or CentOS 7 x86_64 on this machine.
If needed, create a non-root user with sudo access to use for installing the Undercloud:
sudo useradd stack sudo passwd stack # specify a password echo "stack ALL=(root) NOPASSWD:ALL" | sudo tee -a /etc/sudoers.d/stack sudo chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers.d/stack
RHEL
If using RHEL, register the Undercloud for package installations/updates.
RHEL Portal Registration
Register the host machine using Subscription Management:
sudo subscription-manager register --username="[your username]" --password="[your password]"
# Find this with `subscription-manager list --available`
sudo subscription-manager attach --pool="[pool id]"
# Verify repositories are available
sudo subscription-manager repos --list
# Enable repositories needed
sudo subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rpms \
--enable=rhel-7-server-optional-rpms --enable=rhel-7-server-extras-rpms \
--enable=rhel-7-server-openstack-6.0-rpms
RHEL Satellite Registration
To register the host machine to a Satellite, the following repos must be synchronized on the Satellite and enabled for registered systems:
rhel-7-server-rpms
rhel-7-server-optional-rpms
rhel-7-server-extras-rpms
rhel-7-server-openstack-6.0-rpms
See the Red Hat Satellite User Guide for how to configure the system to register with a Satellite server. It is suggested to use an activation key that automatically enables the above repos for registered systems.
Validations¶
You can run the prep validations to verify the hardware. Later in
the process, the validations will be run by the undercloud processes.
However, the undercloud is not set up yet. You can install Ansible on your local machine (that has SSH connectivity to the undercloud) and validate the undercloud from there.
You need Ansible version 2 and the hostname/IP address of the
undercloud (referred to $UNDERCLOUD_HOST here):
$ sudo yum install ansible
$ git clone https://git.openstack.org/openstack/tripleo-validations
$ cd tripleo-validations
$ printf "[undercloud]\n$UNDERCLOUD_HOST" > hosts
Then get the prep validations:
$ grep -l '^\s\+-\s\+prep' -r validations
And run them one by one:
$ ansible-playbook -i hosts validations/validation-name.yaml
Configuration Files¶
instackenv.json¶
Create a JSON file describing your Overcloud baremetal nodes, call it
instackenv.json and place in your home directory. The file should contain
a JSON object with the only field nodes containing list of node
descriptions.
Each node description should contains required fields:
pm_type- driver for Ironic nodes, see Ironic Drivers for detailspm_addr- node BMC IP address (hypervisor address in case of virtual environment)pm_user,pm_password- node BMC credentials
Some fields are optional if you’re going to use introspection later:
mac- list of MAC addresses, optional for bare metalcpu- number of CPU’s in systemarch- CPU architecture (common values arei386andx86_64)memory- memory size in MiBdisk- hard driver size in GiB
It is also possible (but optional) to set Ironic node capabilities directly in the JSON file. This can be useful for assigning node profiles or setting boot options at registration time:
capabilities- Ironic node capabilities. For example:"capabilities": "profile:compute,boot_option:local"
For example:
{
"nodes": [
{
"pm_type":"ipmi",
"mac":[
"fa:16:3e:2a:0e:36"
],
"cpu":"2",
"memory":"4096",
"disk":"40",
"arch":"x86_64",
"pm_user":"admin",
"pm_password":"password",
"pm_addr":"10.0.0.8"
},
{
"pm_type":"ipmi",
"mac":[
"fa:16:3e:da:39:c9"
],
"cpu":"2",
"memory":"4096",
"disk":"40",
"arch":"x86_64",
"pm_user":"admin",
"pm_password":"password",
"pm_addr":"10.0.0.15"
},
{
"pm_type":"ipmi",
"mac":[
"fa:16:3e:51:9b:68"
],
"cpu":"2",
"memory":"4096",
"disk":"40",
"arch":"x86_64",
"pm_user":"admin",
"pm_password":"password",
"pm_addr":"10.0.0.16"
}
]
}
Ironic Drivers¶
Ironic drivers provide various level of support for different hardware. The most up-to-date information about Ironic drivers is at http://docs.openstack.org/developer/ironic/deploy/drivers.html, but note that this page always targets Ironic git master, not the release we use.
This most generic driver is ipmi. It uses ipmitool utility
to manage a bare metal node, and supports a vast variety of hardware.
Stable Branch
This driver is supported starting with the Pike release. For older releases
use functionally equivalent pxe_ipmitool driver.
Virtual
When combined with VirtualBMC this driver can be used for developing and testing TripleO in a virtual environment as well.
Stable Branch
Prior to the Ocata release, a special pxe_ssh driver was used for
testing Ironic in the virtual environment. This driver connects to the
hypervisor to conduct management operations on virtual nodes. In case of
this driver, pm_addr is a hypervisor address, pm_user is a SSH
user name for accessing hypervisor, pm_password is a private SSH
key for accessing hypervisor. Note that private key must not be
encrypted.
Warning
The pxe_ssh driver is deprecated and pxe_ipmitool +
VirtualBMC should be used instead.
Another generic driver is redfish. It provides support for the quite new
Redfish protocol, which aims to replace IPMI eventually as a generic
protocol for managing hardware. In addition to the pm_* fields mentioned
above, this driver also requires setting pm_system_id to the full
identifier of the node in the controller (e.g. /redfish/v1/Systems/42).
Stable Branch
Redfish support was introduced in the Pike release.
Ironic also provides specific drivers for some types of hardware:
pxe_ilotargets HP Proliant Gen 8 and Gen 9 systems, and is recommended for these systems instead ofipmiorpxe_ipmitool. Please refer to the current iLO driver documentation or detailed iLO documentation for Kilo version.pxe_dractargets DELL 11G and newer systems, and is recommended for these systems instead ofipmiorpxe_ipmitool.
There are also 2 testing drivers:
fake_pxeprovides stubs instead of real power and management operations. When using this driver, you have to conduct power on and off operations, and set the current boot device, yourself.fakeprovides stubs for every operation, so that Ironic does not touch hardware at all.

Except where otherwise noted, this document is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. See all OpenStack Legal Documents.