Blazar architecture¶
Blazar’s architecture is described by the following diagram:
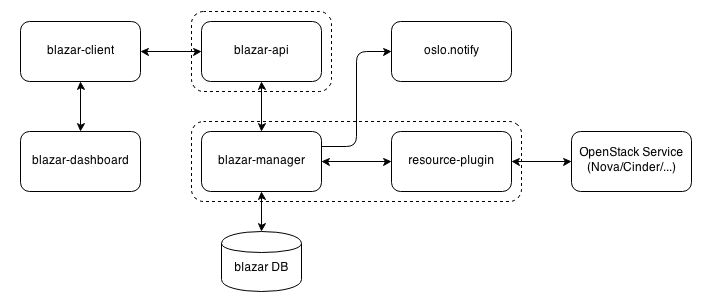
blazar-client - provides a Python implementation of communication with
Blazar API (blazar-api service). It works as a library, a standalone
blazar CLI client, as well as a plugin of the openstack client.
blazar-api - waits for REST API calls from the outside world to redirect
them to the manager. blazar-api communicates with blazar-manager
via RPC.
blazar-manager - implements all logic and operations with leases,
reservations and events. Communicates with Blazar DB and stores there data
on leases, reservations and events.
blazar-manager service is responsible for handling events created for
leases and running all relevant actions. blazar-manager uses
resource-plugins to work with other services’ resources.
resource-plugin - responsible for exact actions to apply to other services’
resources. All resource plugins reside in the same process as
blazar-manager.
Nova resource reservation¶
Blazar’s integration with Nova is based on the following components working in tandem:
Nova
Nova host aggregates are used to control which hosts have their access managed by Blazar. The canonical name for the Blazar-owned host aggregate is
freepool.Nova flavors are used for instance reservations.
Blazar-Nova
The
blazar-novapackage offers theBlazarFilterfilter for nova-scheduler.BlazarFilterensures that Nova does not schedule regular (non-reservation-belonging) instances on Blazar-owned hosts (unless preemption is enabled) and that host lease boundaries are respected.
Placement
Nested resource providers are used to control which hosts are managed by Blazar.
Reservation classes are created and nested resource providers’ inventories are updated for instance reservations.
It is worth noting that Blazar integrations are one-way, i.e. the other services
never call Blazar. Even the BlazarFilter operates in such a way that all
required data is present in Nova and Placement.
Note
Only the compute host reservation is compatible with preemptible instances at the moment.
Compute host reservation¶
Compute host reservation is analogous to a dedicated virtualisation host offering. The user asks for a certain number of hosts with specified characteristics, such as:
the region,
the availability zone,
the host capabilities extra specs,
the number of CPU cores,
the amount of available RAM,
the amount of available disk space.
Matching hosts are reserved for the sole use in the user’s project. Other projects will not share the same hosts during the lease period.
Virtual instance reservation¶
Virtual instance reservation offers a more granular compute resource reservation that does not book entire hypervisors but instead allows using Blazar-owned hosts via special time-limited flavors set up by Blazar. The user asks for a certain number of instances with specific flavor characteristics, such as:
the number of provided CPU cores,
the amount of provided RAM,
the amount of provided disk space,
affinity rule.
When the lease is active, a dedicated flavor is presented to the leasee. No other project may use this flavor. Blazar ensures, albeit in a best-effort manner, that supporting compute resources are reserved, e.g., it will not allow for oversubscribing with multiple reservation types (hosts supporting the virtual instance reservation cannot also be targeted for compute host reservation at the same time).
Flavor-based instance reservation¶
Flavor-based instance reservation is similar in design to virtual instance reservation. However, instead of accepting specific amounts of resources as arguments, the reservation is based on an existing Nova flavor which must be accessible to the user.
Note
The implementation of flavor-based instance reservation is still incomplete. Only a limited number of flavor extra specs is supported. Virtual instance reservations and flavor-based instance reservations cannot yet be created on the same resources. Affinity rules and resource traits are not yet supported.
Neutron resource reservation¶
Apart from compute resources of Nova, Blazar allows to reserve certain Neutron resources. At the moment, these are only floating IPs.
The Neutron integration thus far does not require changes to the Neutron environment. The Blazar interaction looks to Neutron like any other service client interaction.
Floating IPs reservation¶
Blazar admin may register floating IPs with Blazar which can then later be leased to end users. End users request floating IPs from a chosen network and they will be created in user’s project once the lease starts. The allowed floating IPs must not exist in subnet’s allocation pools. Blazar will validate this only once when admin registers the floating IP with Blazar. The integration will break if admin then adds the same floating IP to the allocation pool as Blazar will try to own it and fail.
